Dinalbuphine sebacate (DNS), also known as nalbuphine sebacate or as sebacoyl dinalbuphine ester (SDE) and sold under the brand name Naldebain, is a non-controlled opioid analgesic which is used as a 7-day long-acting injection in the treatment of moderate to severe postoperative pain. It was invented by professor Oliver Yoa-Pu Hu (National Defense Medical Center) and codeveloped with Lumosa Therapeutics. Naldebain received market approvals from Taiwan FDA in March 2017 and Health Sciences Authority of Singapore in December 2020. Development is ongoing in the United States, China, Korea, Thailand, Malaysia. Philippines, and Brunei. The compound is a diester of nalbuphine (Nubain) joined via a sebacic acid linker, and acts as a long-lasting prodrug of nalbuphine via slow hydrolysis. It was developed to extend the duration of action of nalbuphine, which has a short duration and requires frequent injections. Whereas nalbuphine must be injected every 4 to 6 hours, a single injection of DNS lasts for up to 7 to 10 days. Nalbuphine, and hence DNS, acts as a mixed agonist/antagonist opioid modulator, or more specifically as a moderate-efficacy partial agonist or antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a high-efficacy partial agonist of the κ-opioid receptor.
 This DRUG has not been minted yet.
This DRUG has not been minted yet.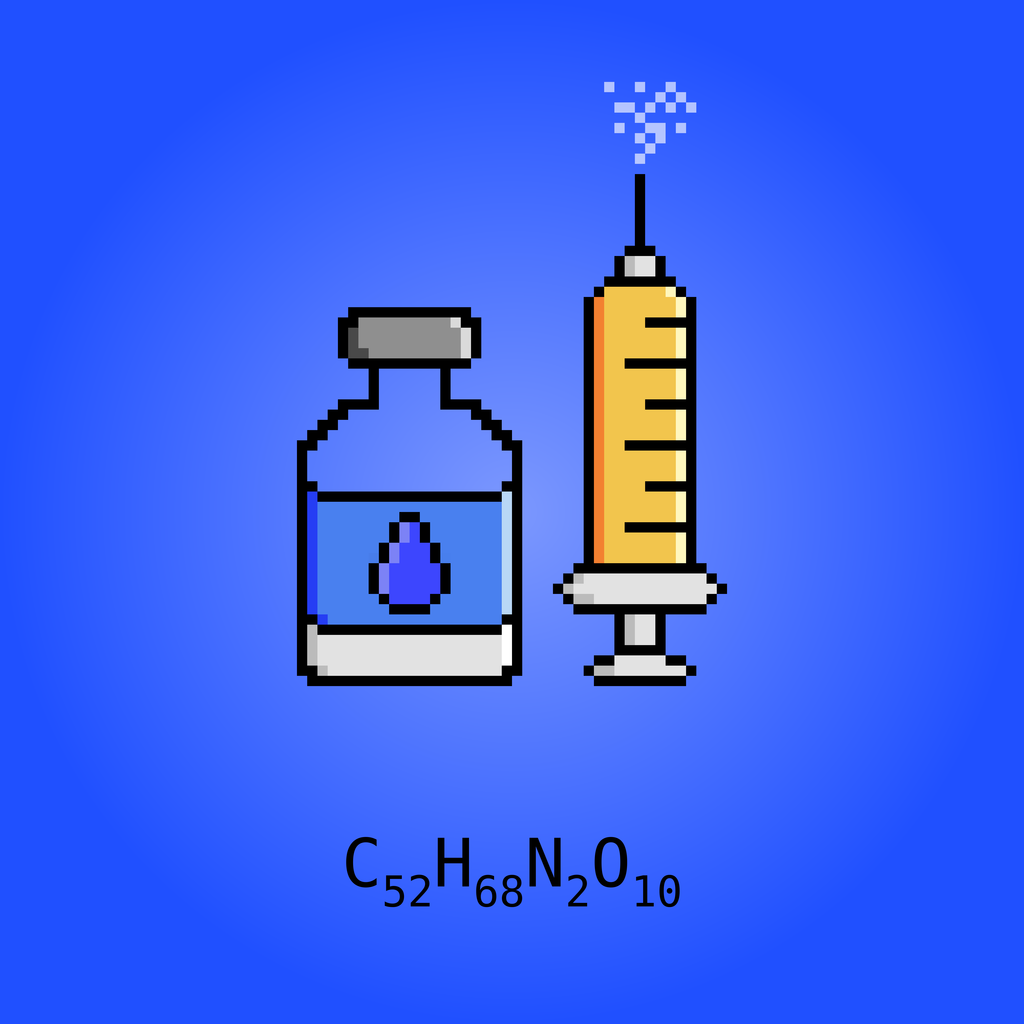
 on Earth by F. Boffa and T. Calemme
on Earth by F. Boffa and T. Calemme